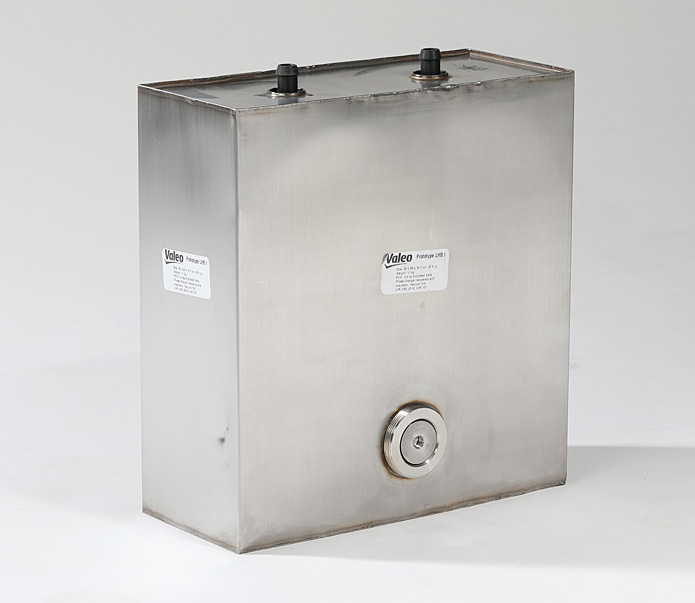
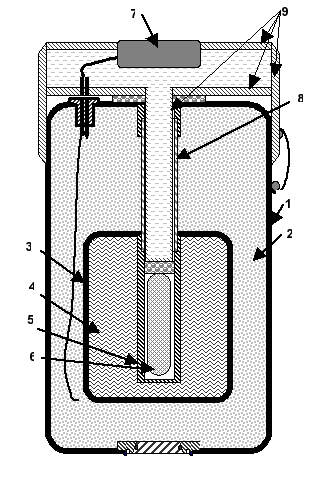
Due to the heat exchange, latent heat accumulators in their current form do not provide an optimum charge or optimum heat discharge. GVI® therefore offers an energy storage unit with a stainless steel housing in which all heat exchanger units are exposed to approximately the same pressure losses, thereby achieving the same volume flows for the individual heat exchanger units. This, in turn, ensures that the same heat flows are supplied to and discharged from the heat exchanger units.
This results in the phase-changing storage units charging and discharging in exactly the same way, making almost optimum heat distribution and energy storage throughout the entire latent heat storage unit possible. The use of vacuum insulation in the highly efficient GVI® systems means that sensitive heat is also stored over long periods. So, for example, seasonal storage systems for solar applications can be realised together with many other application scenarios.
Advantages of the GVI® energy storage system:
- Maximum energy density in a compact design
- Better thermal conductivity
- Storage of more heat energy than with previous solutions
- High chemical resistance